High blood pressure, also known as hypertension, is a prevalent condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Often dubbed the “silent killer,” it often presents no noticeable symptoms, yet it significantly increases the risk of serious health complications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure, and vision loss.
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the world of high blood pressure, providing you with a thorough understanding of its causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and most importantly, effective management strategies. Empower yourself with the knowledge to take control of your health and protect yourself from the silent threat of hypertension.
What is High Blood Pressure?
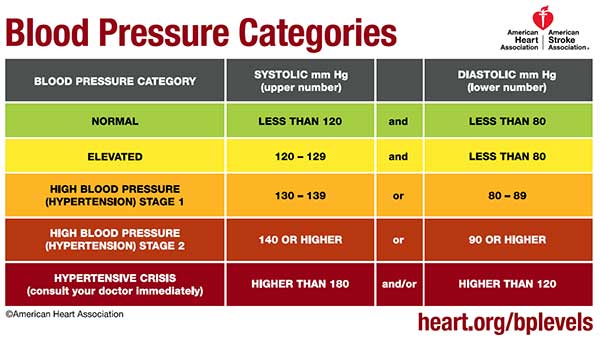
Blood pressure is the force exerted by your blood against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it throughout your body. It is measured in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) with two numbers.
Systolic blood pressure: The top number, represents the pressure when your heart beats and pushes blood out.
Diastolic blood pressure: The bottom number, represents the pressure when your heart rests between beats.
Normal blood pressure is generally considered to be below 120/80 mmHg. High blood pressure is diagnosed when blood pressure consistently reads 130/80 mmHg or higher.
Understanding the Causes: A Multifactorial Condition
High blood pressure is a complex condition with various contributing factors. In many cases, the exact cause remains unknown, but several factors can increase your risk.
Age: Blood pressure tends to rise with age.
Family History: Having a family history of high blood pressure increases your risk.

Lifestyle Factors
Unhealthy Diet: A diet high in sodium, saturated fat, and processed foods can contribute to high blood pressure.
Lack of Physical Activity: Sedentary lifestyles increase the risk.
Obesity: Being overweight or obese puts extra strain on your heart and blood vessels.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can raise blood pressure.
Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases blood pressure.
Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to elevated blood pressure.
Underlying Medical Conditions
Kidney Disease: Kidney problems can disrupt blood pressure regulation.
Diabetes: Diabetes can damage blood vessels and increase the risk of high blood pressure.
Thyroid Disorders: Thyroid conditions can affect blood pressure.
Sleep Apnea: This sleep disorder is associated with high blood pressure.
High Blood Pressure Symptoms
High blood pressure often has no noticeable symptoms, which is why it’s crucial to get your blood pressure checked regularly, especially if you have risk factors. However, in some cases, severe high blood pressure may cause.
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Shortness of Breath
- Nosebleeds
- Flushing
- Chest Pain
If you experience any of these symptoms, seek medical attention immediately.
Diagnosis: Get Regular Checkups
Regular blood pressure checks are essential for early detection and management of high blood pressure. Your doctor will use a blood pressure cuff to measure your blood pressure during a routine checkup. If your blood pressure is elevated, they may recommend further monitoring or testing to confirm the diagnosis.
Managing High Blood Pressure
Managing high blood pressure typically involves a combination of lifestyle modifications and, if necessary, medication.
Lifestyle Modifications
Healthy Diet:
Reduce Sodium Intake: Limit sodium to less than 2,300 milligrams per day, ideally aiming for 1,500 milligrams.
Increase Potassium Intake: Potassium helps counter the effects of sodium. Include potassium-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and legumes in your diet.
Follow the DASH Diet: The Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) diet emphasizes fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and low-fat dairy.
Limit Saturated and Trans Fats: Choose lean protein sources and healthy fats like those found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil.
Regular Exercise
Aim for at Least 150 Minutes of Moderate-Intensity Exercise per Week: Activities like brisk walking, cycling, or swimming can help lower blood pressure.
Include Strength Training: Strength training exercises two to three times a week can also benefit blood pressure.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Lose Weight if You’re Overweight or Obese: Even a small amount of weight loss can significantly lower blood pressure.
Limit Alcohol Consumption – If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation. For men, that means up to two drinks per day, and for women, up to one drink per day.
Quit Smoking
Seek Support to Quit: Smoking cessation programs and medications can help you quit smoking successfully.
Manage Stress
Practice Relaxation Techniques: Incorporate stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, deep breathing, or spending time in nature.
Medications
If lifestyle modifications alone are not enough to control your blood pressure, your doctor may prescribe medication. Several types of blood pressure medications are available, including –
Thiazide Diuretics: Help your body eliminate sodium and water, reducing blood volume.
ACE Inhibitors: Relax blood vessels by blocking the formation of a hormone that narrows them.
Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers (ARBs): Similar to ACE inhibitors, they block the action of the same hormone.
Beta-Blockers: Slow your heart rate and relax blood vessels.
Calcium Channel Blockers: Relax blood vessels and lower heart rate.
Your doctor will determine the most appropriate medication based on your individual needs and health history.
Living with High Blood Pressure: Monitoring and Follow-Up
Managing high blood pressure is an ongoing process. Regular monitoring and follow-up with your doctor are crucial to ensure your treatment plan is effective and to make any necessary adjustments.
Monitor Your Blood Pressure at Home: Home blood pressure monitoring can help you track your progress and identify any potential issues.
Keep Your Doctor Informed: Report any changes in your health or medication side effects to your doctor.
Attend Regular Checkups: Follow your doctor’s recommendations for follow-up appointments and blood pressure checks.
Taking Control of Your Health: Empower Yourself with Knowledge
High blood pressure is a serious condition, but it is manageable. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, you can take control of your health and reduce your risk of complications.
Remember, healthy lifestyle choices are the foundation of blood pressure management. Prioritize a balanced diet, regular exercise, stress management, and healthy habits to protect your heart and overall well-being.






